How to stop “IMAP/POP3 TIME-OUT” e-mail spam
IMAP/POP3 TIME-OUT email spam is a deceptive phishing campaign designed to trick recipients into revealing their email account credentials under the pretense that their email service has been temporarily restricted due to an authentication error. This type of scam typically presents a sense of urgency, urging users to click on links that lead to malicious websites mimicking legitimate email providers. Once users enter their login information, cybercriminals capture these credentials, potentially allowing them access to sensitive personal and financial information. Spam campaigns like this can infect computers in various ways; one common method involves distributing malicious attachments or links within the email. When recipients open these attachments or click on harmful links, they unknowingly initiate the download of malware, which can lead to the theft of data or further system compromise. In some cases, malware can also spread through drive-by downloads that exploit vulnerabilities in browsers or software, reinforcing the need for users to be cautious and vigilant against suspicious emails. Regular updates to antivirus software and safe browsing practices are essential in combating these threats effectively.
How to remove Dice Ransomware and decrypt .dice files
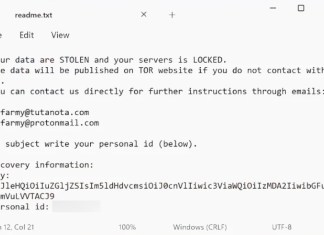
Dice Ransomware is a malicious software designed to encrypt files on an infected computer and demand a ransom for their decryption. This ransomware appends the .dice extension to the original filenames of infected files, turning files such as
document.docx into document.docx.dice. Once the files are encrypted, the malware creates a ransom note titled readme.txt, which it places in various directories to inform the victim of the breach and provide instructions on how to contact the attackers. The note typically threatens that the compromised data will be published on TOR websites if the victim does not pay the ransom. The encryption used by Dice Ransomware is generally robust and often leverages advanced algorithms, making it virtually impossible to decrypt the files without the attackers' decryption key. How to play Call of Duty: Warzone 2.0 on Mac
Call of Duty: Warzone 2.0 is a thrilling battle royale game that builds upon the success of its predecessor, offering an expansive, immersive experience that keeps players on the edge of their seats. Set in a sprawling, dynamic map called Al Mazrah, the game features intense, fast-paced combat with a variety of weapons, vehicles, and tactical equipment at players' disposal. The gameplay emphasizes strategic planning and teamwork, with modes that cater to solo players as well as squads. Warzone 2.0 introduces new mechanics such as the Gulag, where defeated players fight for a chance to re-enter the battle, and contracts that offer in-game objectives for rewards. Its popularity can be attributed to its high-quality graphics, immersive sound design, and the constant updates and seasonal events that keep the content fresh and engaging. The game's cross-platform capabilities also enable a diverse player base to connect and compete. While Warzone 2.0 offers an exhilarating experience for many, Mac users face challenges in running the game natively due to the lack of official support. However, with the use of third-party software or platform virtualization, some Mac gamers may still find ways to join the action.
How to stop “Foreign Beneficiary” e-mail spam
Foreign Beneficiary email spam refers to deceptive phishing emails that lure recipients with promises of large sums of money, often claiming to be a legitimate offer to claim funds from a deceased individual’s bank account. These emails typically present a fabricated story involving a foreign beneficiary and an unclaimed fortune, urging the recipient to provide personal information or send money upfront for fees or taxes. Spam campaigns often infect computers by distributing malicious files as attachments or links within these emails, exploiting the trust of unsuspecting users. Once an individual clicks on a link or opens an attachment, malware can be downloaded, initiating an infection chain that may lead to unauthorized access to personal information and sensitive data. Cybercriminals employ various tactics, such as using deceptive email addresses or creating urgency through alarming messages, to increase the likelihood of victims falling for their scams. Moreover, malicious files can come in different formats, including documents or executables, which may require additional user interaction to activate. Therefore, vigilance is crucial when dealing with unsolicited emails to prevent becoming a victim of such scams.
How to stop “Yahoo Canada Lottery” e-mail spam
Yahoo Canada Lottery email spam is a deceptive phishing scheme designed to trick recipients into believing they have won a substantial cash prize, often claiming a fictitious amount like five million USD. These emails typically instruct users to provide personal information, such as their name, address, and financial details, under the pretense of claiming the prize. Many individuals fall for this ruse, inadvertently disclosing sensitive information that can lead to identity theft and financial loss. Spam campaigns often spread malware through malicious attachments or links embedded within the messages. When a user opens an attachment or clicks on a link, they may unknowingly initiate a download of harmful software, such as trojans or ransomware, that compromises their system. Additionally, some emails may employ social engineering tactics to create a sense of urgency, pressuring users to act quickly without considering the risks. Therefore, it is crucial for users to remain vigilant and skeptical of unsolicited emails, especially those that promise large sums of money or require personal information.
How to stop “Samsung Prize Money” e-mail spam
Samsung Prize Money email spam is a deceptive phishing campaign designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive personal information by claiming they have won a monetary prize from a Samsung promotion. These emails often boast impressive sums, such as $800,000, and instruct users to provide their myGov account details to claim their "winnings." Such scams exploit the trust of individuals by mimicking legitimate organizations, thereby increasing the likelihood of falling victim to the deception. Spam campaigns can infect computers in various ways, primarily through malicious attachments or links embedded within the emails. When a user opens an infected attachment or clicks on a dubious link, malware can be downloaded and installed without their knowledge. This malware can then steal sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details, leading to identity theft and financial loss. Moreover, some campaigns may use social engineering tactics, manipulating emotions or urgency to prompt users into taking immediate action, thereby bypassing their better judgment. Ultimately, vigilance and skepticism toward unsolicited emails are crucial in avoiding such scams and protecting personal information.
How to remove Insom Ransomware and decrypt .insom files
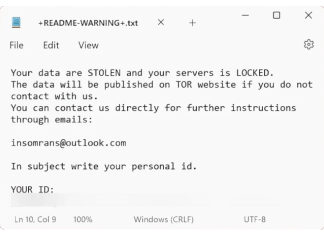
Insom Ransomware is a potent form of malware that belongs to the Makop family, a notorious group known for encrypting users' files and demanding a ransom for their decryption. When it infects a system, it appends a unique identifier, the attacker's email address, and the .insom extension to the locked files. For instance, a file named
photo.jpg would be renamed to something like photo.jpg.[ID].[attacker@domain.com].insom. This ransomware typically uses strong encryption algorithms, making the decryption of affected files very difficult without the attacker's decryption key. After encrypting the files, it drops a ransom note named README-WARNING+.txt, which typically appears on the desktop and in directories containing encrypted files. The note usually warns victims about the encryption of their data and threatens to publish or permanently encrypt their files unless the ransom is paid. How to remove Allock Ransomware and decrypt .allock8 files
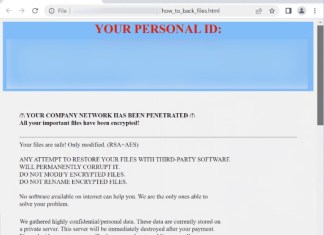
While inspecting new submissions to VirusTotal, researchers identified Allock Ransomware, a member of the MedusaLocker ransomware family. It renames files with a specific extension, notably .allock8, which can vary with the virus iteration. The ransomware employs sophisticated RSA+AES encryption, making file recovery difficult without the attackers' involvement. Upon completion of the encryption process, it creates a ransom note named how_to_back_files.html and places it prominently on the desktop. This note informs victims of the data breach and demands payment for the decryption tools, along with the threat of leaking or selling stolen data if payment isn't made.