How to remove ETHAN Ransomware and decrypt .ETHAN files
ETHAN Ransomware is a malicious software threat classified under the MedusaLocker ransomware family. It is specifically designed to infiltrate computer networks, encrypt files, and demand ransom payments from victims in exchange for file decryption. This ransomware uses a combination of RSA and AES cryptographic algorithms, which are often employed to ensure that once data is encrypted, decryption becomes exceedingly difficult without the correct key. In a typical attack, files on an infected system are targeted for encryption, and as part of this process, their original filenames are altered by appending the extension .ETHAN — for instance, a file named
document.docx becomes document.docx.ETHAN. Following the encryption, READ_NOTE.html, a ransom note file, is generated and placed in various locations on the affected system, often accompanied by changes to the desktop wallpaper to further alert the user to the breach. This ransom note informs victims that their files have been encrypted and that personal or company data might have been exfiltrated, thus exerting additional pressure to comply with the payment demands. How to remove Marcher Banking Trojan (Android)
Marcher Banking Trojan is a sophisticated malware targeting Android devices, primarily designed to steal sensitive banking information. It operates by overlaying legitimate applications with deceptive screens that mimic genuine login pages, tricking users into providing their credentials. Since its emergence in 2013, Marcher has evolved, incorporating various functionalities that allow it to monitor device activity and collect personal data. This malware can request extensive permissions, such as controlling system settings and accessing external storage, which enhances its capability to execute malicious tasks. It has also been linked to tactics like phishing and drive-by downloads, often leveraging fake updates or malicious links to infiltrate devices. With its ability to intercept SMS messages, Marcher can capture one-time passwords and two-factor authentication codes, significantly increasing the risk of financial theft. Users experiencing symptoms such as slowed performance, unexpected battery drain, or unfamiliar applications should consider scanning their devices for this dangerous trojan. Effective prevention measures include using reputable antivirus software, avoiding suspicious links, and regularly updating device software.
How to remove Cowboy Stealer
Cowboy Stealer is a sophisticated piece of malware designed to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive information, particularly targeting cryptocurrency wallets. Written in the Go programming language, it is capable of extracting stored credentials, private keys, and other critical data, enabling cybercriminals to access victims' digital assets. This malware can capture screenshots, allowing attackers to steal private messages, authentication codes, and other sensitive information. Additionally, Cowboy Stealer can harvest data from web browsers, such as saved login credentials and browsing history, as well as monitor clipboard activities to capture copied cryptocurrency addresses and credit card numbers. Its keylogging feature further allows it to record every keystroke made on an infected device, posing a significant threat to users' privacy and security. Often distributed through malicious email attachments, deceptive websites, and infected software, Cowboy Stealer operates stealthily, making it difficult to detect without advanced security solutions. Prompt removal and strong preventive measures are essential to protect against this severe threat, ensuring that systems remain secure from unauthorized access and data theft.
How to remove CipherLocker Ransomware and decrypt .clocker files
CipherLocker Ransomware is a malicious software program designed to encrypt files on an infected computer, effectively rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Victims will notice that encrypted files have the extension .clocker appended to their original filenames, indicating that they are under the ransomware's lock. For example, a file named
example.docx would appear as example.docx.clocker once encrypted. Typically employing robust encryption algorithms, CipherLocker Ransomware makes decryption without a specific key practically impossible. This ransomware drops a ransom note titled README.txt in the infected directories, which informs the victim of the situation and demands a payment of Bitcoin to restore access to the files. The note often includes detailed payment instructions, a deadline, and a warning against attempting to decrypt the files using unauthorized software, underscoring the potential loss of data. How to remove Qqqw Ransomware and decrypt .qqqw files
Qqqw Ransomware is a malicious software variant that belongs to the notorious Djvu family of ransomware. This malware is specifically designed to encrypt files on a victim's computer, rendering them inaccessible without a decryption key. Once it infiltrates a system, it appends the .qqqw extension to the affected files, effectively locking users out of their own data. For instance, a file named
document.txt would be renamed to document.txt.qqqw. This ransomware uses a sophisticated encryption algorithm, making it extremely difficult for victims to regain access to their data without the cybercriminals' intervention. After encryption, the ransomware generates a ransom note titled _readme.txt, which is typically placed in every folder containing encrypted files. This note provides instructions on how victims can contact the attackers to pay the ransom, which is often demanded in Bitcoin, in exchange for a decryption key. How to remove Vgod Ransomware and decrypt .Vgod files
Vgod Ransomware emerges as a notorious ransomware variant that encrypts user files, rendering them inaccessible to extort money from unsuspecting victims. This malware typically appends the .Vgod extension to all encrypted files, making them instantly recognizable to their unfortunate owners. Users might find familiar files such as
photo.jpg transformed into photo.jpg.Vgod, highlighting the extent of the encryption. Ransomware like this usually employs complex encryption algorithms, often relying on advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure that decryption without the appropriate keys is virtually impossible. When victims discover their systems compromised, they encounter a ransom note named Decryption Instructions.txt, strategically placed in various folders across the infected system, including the desktop. This note informs victims of the encryption, provides a unique decryption ID, and demands that they contact the attackers via email, typically including instructions to pay a ransom in exchange for the recovery tool and key. How to remove FrigidStealer (Mac)
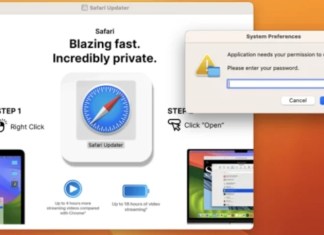
FrigidStealer is a sophisticated piece of malware targeting macOS, primarily designed to exfiltrate sensitive user information. It typically infiltrates systems through deceptive campaigns masquerading as legitimate browser updates for Safari or Google Chrome, effectively bypassing Mac's Gatekeeper security feature. Once installed, this stealer discreetly harvests critical data, including login credentials, cryptocurrency wallet information, and internet cookies, posing a significant risk to user privacy and financial security. Its modus operandi involves searching through the Desktop and Documents folders for files with specific keywords, further highlighting its targeted nature. Moreover, FrigidStealer's capability to extract entries from Mac's native Notes application underscores its threat level, as it can lead to identity theft and financial losses. The absence of overt symptoms makes it particularly insidious, allowing it to operate undetected while compromising system integrity. It is crucial for users to employ reputable antivirus solutions and practice safe browsing habits to mitigate the risks associated with this potent malware.
How to remove Zhong Stealer
Zhong Stealer is a sophisticated piece of malware designed to infiltrate Windows systems and discreetly steal sensitive user information. It operates by utilizing various stealth techniques, ensuring it remains undetected by typical security measures. Once it infects a system, the malware targets data stored in popular web browsers like Brave, Edge, and Internet Explorer, extracting saved passwords, browser session data, and authentication tokens. Cybercriminals use this stolen information to gain unauthorized access to victims' online accounts, potentially leading to financial fraud, identity theft, and further exploitation. The malware is primarily distributed through targeted phishing campaigns, often aimed at the cryptocurrency and fintech sectors, leveraging social engineering tactics to trick users into executing malicious files. Zhong Stealer's ability to disable security logs and maintain persistence on infected systems makes it a severe threat, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity practices. Regular updates to software and operating systems, alongside the use of reputable antivirus tools, are crucial in mitigating the risks associated with such advanced threats.