How to remove Frag Ransomware and decrypt .frag files
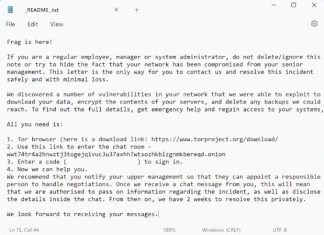
Frag Ransomware is a sophisticated form of malicious software that infiltrates digital systems, primarily those of companies, and encrypts crucial data to extort a ransom payment from the victims. This ransomware appends the .frag file extension to the names of the encrypted files, effectively locking them and rendering them unusable without a decryption key. For instance, a document initially named
report.docx would become report.docx.frag. Once the encryption process is complete, Frag Ransomware generates a ransom note in a text file strategically named README.txt, which is typically placed within the affected directories or even on the desktop. The note ominously informs the victim that their files have been encrypted and demands a ransom in exchange for a decryption key. Unfortunately, as of the latest advisories, there are no publicly available decryption tools specifically for Frag Ransomware, making file recovery without a backup a Herculean task. How to remove ElizaRAT
ElizaRAT is a sophisticated Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that poses a severe threat to computer systems by allowing cybercriminals to remotely control infected devices. Developed in .NET, ElizaRAT has been utilized in various cyber-espionage campaigns, leveraging cloud services like Slack, Telegram, and Google Drive for its command-and-control operations. Its primary function is to steal sensitive data, making it a potent tool for attackers seeking to exfiltrate confidential information from victims. Over time, ElizaRAT has evolved, incorporating new features such as ApoloStealer and ConnectX, which enhance its capability to collect and exfiltrate files stealthily. This malware operates silently, often leaving no visible symptoms on infected machines, thereby prolonging its presence and amplifying the potential damage. Its distribution typically occurs through phishing emails, malicious advertisements, and software cracks, making it crucial for users to practice caution and employ robust security measures. As a persistent threat, ElizaRAT underscores the importance of using reliable antivirus solutions to detect and remove such infections, safeguarding against the severe risks of identity theft and financial loss.
How to remove Winos4.0 Malware
Winos4.0 Malware is a sophisticated malicious framework that attackers deploy to conduct varied and multi-functional infections, primarily operating as a backdoor. This type of malware is known for its ability to introduce additional malicious modules into an infected system, significantly expanding its capabilities. The initial infection often masquerades as legitimate software, such as gaming applications, to deceive users. Once installed, Winos4.0 can perform a range of malicious activities, including data theft, executing commands, and downloading further harmful programs. It targets sensitive information, including device data, crypto-related browser extensions, and can potentially lead to severe privacy breaches and financial losses. The distributed nature of its modules allows it to adapt its functionalities across different attacks, making it a persistent threat. Its stealthy infiltration techniques often leave victims unaware of its presence, leading to long-term consequences like identity theft and system compromise.
How to remove Scp Ransomware and decrypt .scp files
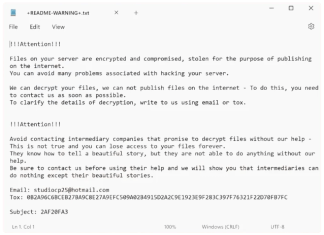
Scp Ransomware is a malicious program that belongs to the Makop family of ransomware. This particular strain has been observed to encrypt files on a victim's computer, rendering them inaccessible and unusable until a ransom is paid. Upon encryption, the ransomware appends a unique file extension to each affected file, which includes the victim's ID, an email address, and the distinctive .scp suffix. For instance, an original file named
document.docx might be altered to document.docx.[ID].[email].scp. The encryption process typically utilizes sophisticated algorithms that ensure the affected files cannot be opened or modified without the decryption key known only to the attackers. Once the encryption is complete, Scp Ransomware changes the desktop wallpaper to alert the user of the infection and to further stress the gravity of the situation.тFollowing the encryption, a ransom note is generated in a file titled +README-WARNING+.txt, which is often strategically placed on the desktop or within affected directories for visibility. How to remove Mac Cryptominer
Mac Cryptominer is a type of malware that infiltrates Mac systems to hijack computing resources for cryptocurrency mining without the user's consent. This malicious software typically deploys stealthy tactics to run in the background, unnoticed, increasing the CPU workload significantly. As it utilizes a substantial portion of the system's processing power, users may experience a noticeable slowdown in performance, frequent system crashes, and unexpected shutdowns due to overheating. This excessive resource consumption not only degrades the overall functionality of the device but also leads to increased electricity bills. Over time, the constant strain on hardware components can cause irreversible damage, necessitating costly repairs or replacements. The cryptominer typically infiltrates systems through bundled software downloads, fake update alerts, or malicious email attachments. To protect against such threats, users should exercise caution during software installations, avoid dubious download sources, and employ robust antivirus solutions to detect and eliminate potential infections.
How to remove VIPxxx Ransomware and decrypt .VIPxxx files
VIPxxx Ransomware is a severe type of malware designed to deprive users of access to their data by encrypting files on compromised systems. Victims of this ransomware find their files renamed, with extensions altered to include a unique identifier, an appended email address, and the suffix .VIPxxx. For instance, a file initially named
document.jpg might appear as document.jpg.[ID-123456].[cmd_bad@keemail.me].VIPxxx post-attack. The encryption is sophisticated, typically employing strong cryptographic algorithms that render files completely inaccessible without a specific decryption key. This encryption method is often irreversible without cooperation from the perpetrators, who are the only holders of decryption credentials. Accompanying this malicious activity is a ransom note, commonly named RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt. This file is strategically placed in each folder containing encrypted files, serving as a communication channel between the attackers and their victims. The note coerces users to contact the cybercriminals, often suggesting that only they can provide the necessary decryption tools in exchange for a cryptocurrency payment. How to remove CryptoAITools Malware
CryptoAITools Malware is a sophisticated Trojan designed to infiltrate both Windows and Mac operating systems under the guise of a cryptocurrency trading tool. This malicious software is primarily distributed through the Python Package Index (PyPI) and GitHub, masquerading as a legitimate application to lure unsuspecting users. Once installed, it creates a deceptive interface that simulates cryptocurrency trading activities while secretly executing data theft in the background. It targets sensitive information such as browsing history, saved login credentials, internet cookies, and data from crypto wallets including Atomic, Bitcoin, and Ethereum, among others. This malware also has the capability to exfiltrate files related to cryptocurrencies and financial data from common directories like Downloads and Documents. Threat actors behind CryptoAITools further enhance its functionality by downloading additional malicious payloads from a controlled website, coinsw[.]app, which poses as a legitimate crypto-trading bot service. The primary goal of this malware is to steal cryptocurrency, posing significant risks of financial loss and identity theft for affected users. As CryptoAITools evolves, it may develop new capabilities, making early detection and removal crucial to prevent severe damage.
How to remove Interlock Ransomware and decrypt .interlock files
Interlock Ransomware is a notorious form of malware that wreaks havoc by encrypting the files of its victims, demanding a ransom for their return. This ransomware has been detected on both Windows and Linux systems, marking its broad scope of attack. Upon infecting a machine, it appends the .interlock extension to the end of each affected file. This means that if you have a document named
report.docx, it will be altered to report.docx.interlock, rendering it inaccessible. The encryption method used by Interlock is sophisticated, employing advanced cryptographic techniques, which makes the files impossible to decrypt without the decryption key. After the encryption process is complete, the ransomware drops a ransom note titled !__README__!.txt onto the infected system. This note is typically placed in prominent locations, such as the desktop or in directories containing encrypted files, and it details the attack, providing instructions for payment and warning against modifying affected files.