How to remove MAGA Ransomware and decrypt .MAGA files
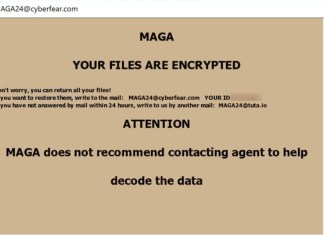
MAGA Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on an infected computer and demands a ransom for their decryption. This ransomware is part of the Dharma family, known for appending a unique combination of identifiers to each file name to signify that they have been encrypted. Specifically, it adds an extension that includes the victim's unique ID, an attacker’s email address, and the .MAGA file extension, transforming a file like
document.docx into something like document.docx.id-J0CFK89P.[MAGA24@cyberfear.com].MAGA. For encryption, MAGA utilizes sophisticated algorithms that convert the files into an unreadable form, making it almost impossible to access them without a specific decryption key. The ransomware drops a ransom note within the infected system, typically as a pop-up message and as a text file named MAGA_info.txt, which instructs the victim to contact the attacker via email for file recovery instructions and warns against seeking third-party help. How to remove ViT Ransomware and decrypt .ViT files
ViT Ransomware is a malicious program identified as part of the Xorist ransomware family. It primarily targets user files, encrypting them to demand a ransom payment for their release. Upon infection, ViT appends the encrypted files with a distinctive file extension, .ViT, making them inaccessible. For example, a file originally named
photo.jpg would be renamed to photo.jpg.ViT, rendering it useless without a decryption key. The ransomware uses a combination of symmetric and potentially asymmetric encryption algorithms to ensure that the data is securely locked, thus complicating the decryption process without the appropriate key held by the cybercriminals. Once the files are encrypted, ViT generates a ransom note, typically named HOW TO DECRYPT FILES.txt, which is deposited in each folder containing encrypted files. Additionally, a pop-up window is displayed to the victim, reinforcing the ransom demand and instructing them to make a payment, usually in Bitcoin, to a specified wallet. How to remove Revive Ransomware and decrypt .revive files
Revive Ransomware is a malicious software entity that specifically targets user data to extort money. Originating from the Makop family of ransomware, it encrypts files to render them inaccessible, subsequently demanding that victims pay a ransom for the decryption key. During its encryption process, the ransomware appends each file name with a unique identifier followed by the attackers' email address and concludes with the .revive extension. For instance, a file initially named
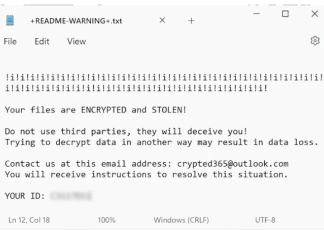
document.txt would transform into document.txt.[uniqueID].[attackerEmail].revive on an infected system. The ransomware primarily employs sophisticated cryptographic algorithms, often making the decryption of files extremely challenging without the appropriate tools. After the encryption phase, Revive ransomware leaves behind a ransom note in the form of a text document titled +README-WARNING+.txt, which typically appears in directories with encrypted files. This note advises victims to contact the attackers directly for decryption instructions, warning against third-party attempts to unlock the data as purportedly leading to permanent loss. How to remove Scarab-Walker Ransomware and decrypt .JohnnieWalker files
Scarab-Walker Ransomware is a malicious software variant belonging to the notorious Scarab ransomware family, known for encrypting files on victimized systems to extort money from its victims. When this ransomware infiltrates a computer, it scans the system for a wide array of file types such as documents, PDFs, images, videos, and databases, making them inaccessible by using strong encryption algorithms. Upon encryption, these files are appended with the distinctive .JohnnieWalker extension, signifying that they have been compromised. The specific encryption method used by Scarab-Walker is robust enough to prevent simple decryption attempts without the corresponding decryption key, which is why it becomes crucial for affected users to look for specialized decryption solutions rather than attempting random file recovery methods. Once the encryption process is complete, a ransom note is generated, usually placed in all folders containing affected files, as well as the desktop, to ensure visibility to the user. This ransom note, typically named HOW TO DECRYPT WALKER INFO.TXT, provides instructions for victims on how to contact the attackers and make a ransom payment - often demanded in Bitcoin - in exchange for the supposed decryption key.
How to remove Scarab-Bin Ransomware and decrypt .bin or .lock files
Scarab-Bin Ransomware is a malicious software variant that belongs to the extensive family of Scarab Ransomware. This file-encrypting malware typically infiltrates systems through phishing emails or malicious attachments, often masquerading as benign correspondence to unsuspecting users. Once access is gained, the ransomware begins encrypting files on the infected system using advanced encryption algorithms, primarily targeting a wide range of file types including documents, spreadsheets, and databases. Users will notice a change in file extensions, as the ransomware appends .bin or .lock to the compromised files, rendering them inaccessible. Following the encryption process, Scarab-Bin leaves a ransom note titled HOW TO RECOVER ENCRYPTED FILES.TXT within various folders, urging victims to contact the attackers via email for decryption instructions. The note typically includes a personal identifier and demands payment in cryptocurrency to recover access to the files.
How to remove GandCrab v4.1 Ransomware and decrypt .krab files
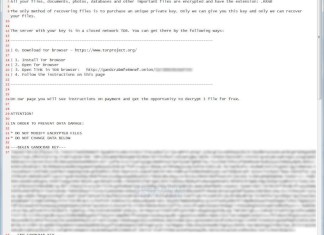
GandCrab v4.1 Ransomware represents a formidable evolution in the realm of cyber threats. As a part of the notorious GandCrab ransomware family, this version continues to employ advanced encryption techniques, specifically using AES-256 and RSA-2048 algorithms, to secure its hold over victims' files. Victims will notice that files previously accessible suddenly bear a new extension, specifically the .krab extension, rendering them unreadable without the decryption key. The ransomware stealthily infiltrates systems, often through vulnerabilities such as unprotected Remote Desktop Protocol connectors or through malicious email attachments and links. It further erases shadow copies from the system, which exacerbates the difficulty in restoring data. Upon successful encryption, GandCrab leaves behind a ransom note named krab-decrypt.txt on the infected machine. This note informs victims about the compromised state of their files and provides instructions to access a site via the TOR network. Victims are urged not to modify encrypted files, as these could become permanently damaged beyond recovery.
How to remove Scarab-CyberGod Ransomware and decrypt .CyberGod files
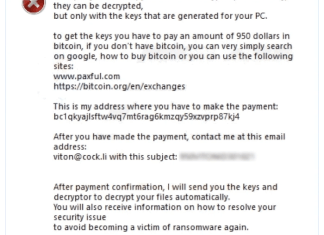
Scarab-CyberGod Ransomware is a malicious cryptovirus, belonging to the notorious Scarab Ransomware family. It infiltrates computers, encrypting user files and rendering them inaccessible. Victims of this ransomware will find their files with the new .CyberGod extension, indicating they have been encrypted. The malware employs strong encryption algorithms, making it difficult for users to decrypt their files without the attacker's key. Once the file encryption process is complete, the ransomware leaves a ransom note titled From Jobe Smith.TXT. This note can typically be found in every directory where files have been encrypted. The note contains payment instructions and threatens the permanent loss of data unless the ransom is paid, often amounting to several hundred dollars. Victims are urged not to trust these cybercriminals, as paying the ransom does not guarantee data recovery.
How to remove FenixLocker Ransomware and decrypt .centrumfr@india.com files
FenixLocker Ransomware is a malicious software that encrypts files on infected systems, rendering them inaccessible to the user. This ransomware typically adds the .centrumfr@india.com extension to the compromised files, which serves as a clear indicator of infection. Among other possible extensions for this ransomware are: .[help24decrypt@cock.li], .help24decrypt@qq.com!!. Through its process, it employs AES cryptography, a robust encryption method that effectively ensures the victim cannot access their data without the decryption key. After encrypting the files, FenixLocker leaves a ransom notes titled Help to decrypt.txt or Cryptolocker.txt on the desktop. The note instructs victims to contact the attackers via email to receive further steps, often requesting a ransom in Bitcoin to restore access to the files. Despite the compelling nature of these notes, paying the ransom is highly discouraged since it doesn't guarantee the decryption of files and may further expose victims to additional risks.